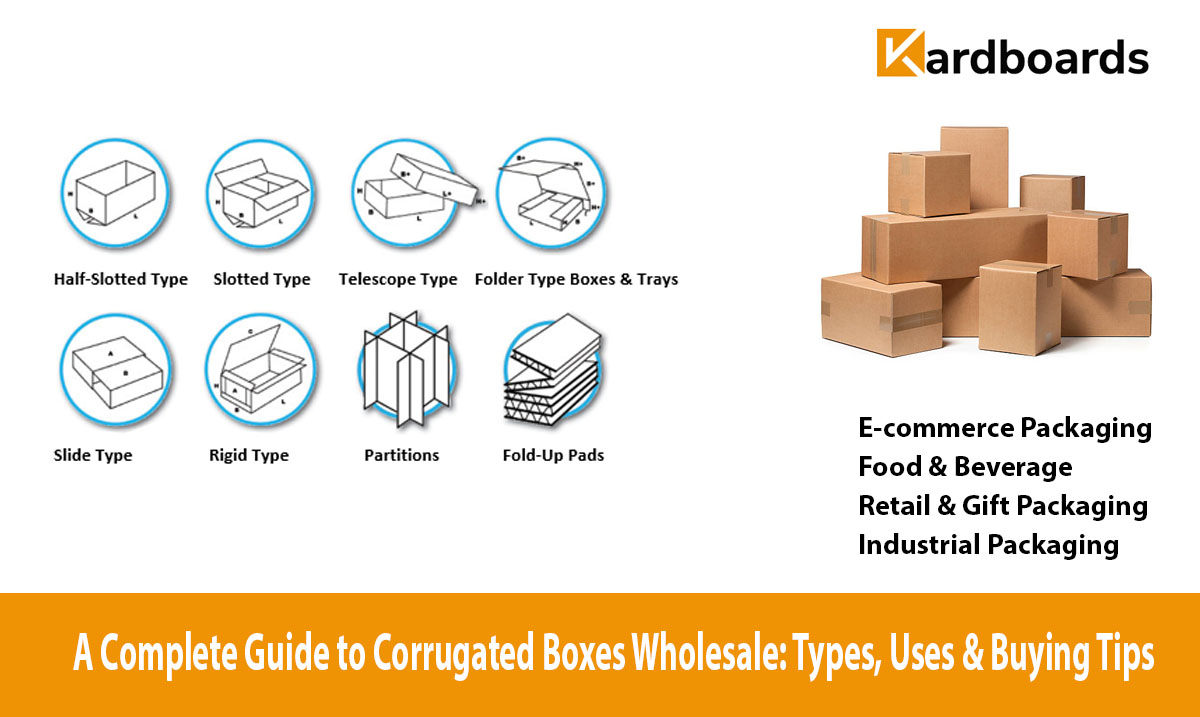
Corrugated boxes are expected to do two things exceptionally well: protect the product and do so economically. Leading corrugated box manufacturers achieve this balance by combining engineered materials, optimized box design, automated production, and stringent quality control. Below we unpack the technical steps and commercial strategies that deliver strength, durability and cost-efficiency at scale.
1. Material Engineering: Paper Grades, Liners & Flutes
Strength starts with raw materials. Manufacturers choose linerboards and corrugating mediums tailored to the product’s needs:
- Liner quality: Kraft liners (brown or white) with higher burst and tensile strength improve edge compression and stacking resistance.
- Flute selection: A, B, C, E and hybrid combinations (e.g., BC, EB) balance cushioning, stacking strength and printability — C-flute is common for shipping; E-flute for retail presentation.
- Number of plies: Single-wall for light goods, double- and triple-wall constructions for heavy or export-grade shipments.
Tip: The right combination of flute type and ply can often replace more expensive board grades while delivering equivalent performance — a key lever for cost optimization.
2. Precision Manufacturing: Corrugators, Adhesives & Process Control
Modern corrugation lines are highly controlled systems. Critical process controls include:
- Corrugator settings: Temperature, steam, and web tension are tuned to produce consistent flute profiles and strong bond between flute and liners.
- Adhesive application: Controlled glue patterns and correct starch concentrations ensure durable bonding without excess material waste.
- Inline trimming & slitting: Accurate cutting minimizes waste and enables tight nesting to maximize yield from paper rolls.
3. Structural Design & Right-Sizing
Engineering the box geometry is a major contributor to both strength and cost-efficiency:
- Right-sizing: Reducing empty volume lowers material use and shipping cost (dimensional weight savings).
- Structural reinforcement: Reinforced corners, double-folded flaps, and internal partitions increase crush resistance without large material up-specs.
- Nesting & layout: Smart die layouts and nesting reduce paper waste and improve throughput.
4. Testing & Quality Assurance
To guarantee durability in real-world conditions, manufacturers run standard tests and custom validation:
- Edge Crush Test (ECT): Measures stacking resistance — a core predictor of how boxes behave in pallets.
- Burst (Mullen) Test: Evaluates rupture strength and the ability to withstand impact.
- Compression testing: Verifies load-bearing capacity under vertical pressure.
- Drop and transit simulation: Lab drop tests and vibration tables simulate e-commerce and distribution handling.
- Moisture & environmental tests: Checks coatings and treatments for humid or marine conditions.
5. Automation & Process Efficiency
Automation reduces variability and labor costs while increasing speed:
- Automated die-cutters and folder-gluers deliver precise cuts and consistent gluing at high speed.
- Robotic stacking and palletising reduce handling damage and speed up loading for export containers.
- Inline inspection (camera-based) finds print defects or structural faults early, lowering rework rates.
6. Coatings, Treatments & Performance Enhancements
Surface treatments and specialized coatings help boxes survive moisture, abrasion and long transit:
- Moisture-resistant coatings: Waxy or water-resistant coatings protect board integrity in humid environments.
- Anti-slip coatings: Improve pallet stability and reduce toppling risk in stacked loads.
- Surface finishes: Varnishes, laminates and UV treatments add print durability and premium appearance when required.
7. Cost Optimization Strategies
Manufacturers continually drive cost-efficiency through:
- Material optimization: Matching flute and ply precisely to need avoids over-specification.
- Yield improvement: Better roll layouts, reduced trim, and efficient cutting lower material waste.
- Volume purchasing: Bulk procurement of paper and adhesives reduces input costs which can be passed to buyers.
- Energy & process optimization: Modern lines consume less steam and electricity per square meter of board produced.
8. Sustainability — Strength Without Excess Waste
Leading producers blend recycled fibre usage with industrial process controls to maintain performance while reducing environmental impact. Programs include:
- High recycled-content liners where appropriate
- Use of water-based and low-VOC inks
- Design-for-recyclability (avoid mixed-material laminates where possible)
9. Practical Tips for Buyers
- Request test reports: ECT, BCT and compression test certificates for the supplied board.
- Order samples: Real-life samples allow drop testing with your product and transit simulation.
- Discuss right-sizing: Share product dimensions and packaging goals — manufacturers can help reduce material and shipping cost.
- Check supplier automation & QC: Ask about inline inspection, camera checks and pre-shipment audits.
- Consider total landed cost: Factor material, shipping (dimensional weight), and damage rates — cheaper boxes that cause returns cost more in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do flute types affect box strength?
Different flute profiles offer trade-offs between cushioning, stacking strength and printability. C-flute offers a balance for shipping; E-flute is thinner and better for high-quality printing.
What is the most important test for stacking strength?
Edge Crush Test (ECT) and compression testing are the best indicators of how a box will perform under palletised loads.
Can automation actually lower box prices?
Yes — automation reduces labor, improves yield and cuts rework, which lowers production cost and often reduces buyer prices.
Is recycled board as strong as virgin board?
Modern recycled boards can meet performance targets when designed correctly; however, certain heavy-duty or moisture-critical applications may still prefer higher-grade or virgin fibres.