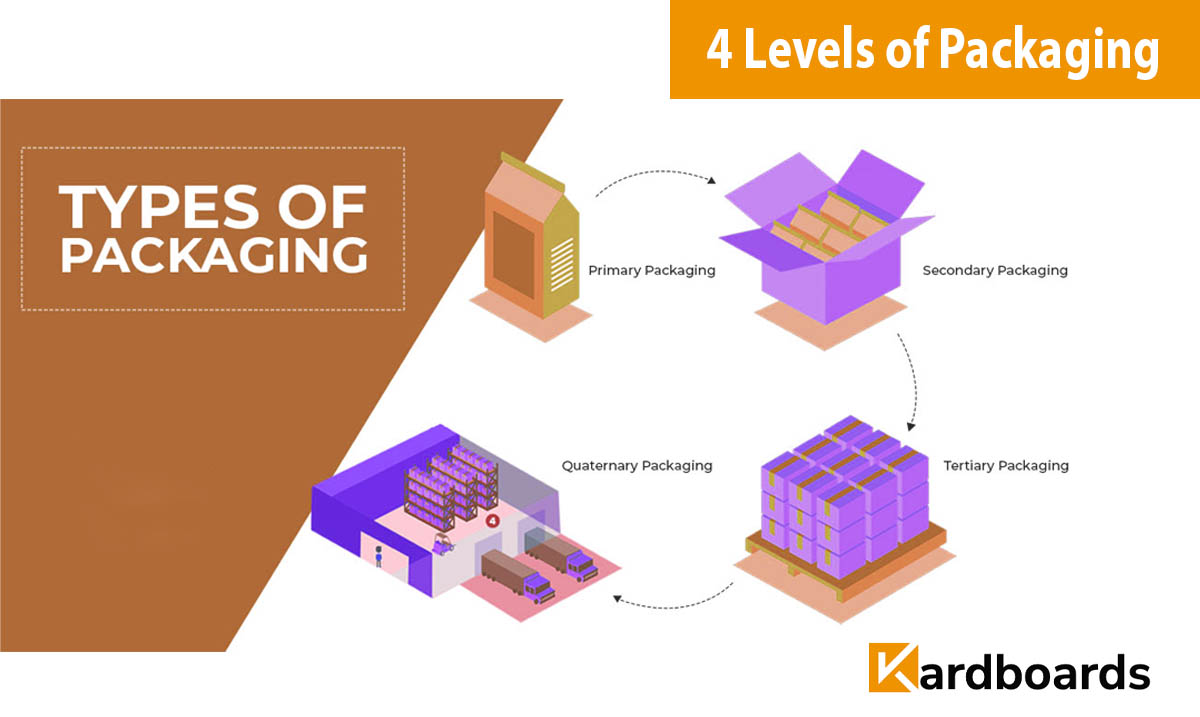
Packaging serves as a bridge between products and consumers — ensuring safety, usability, and branding at every stage. To manage this complexity, the industry classifies packaging into four distinct levels: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary Packaging.
Each level has its own function within the product’s lifecycle — from individual product protection to large-scale logistics. Kardboards designs and manufactures packaging that integrates all four levels with precision, sustainability, and global standards.
1. Primary Packaging — The First Layer of Protection
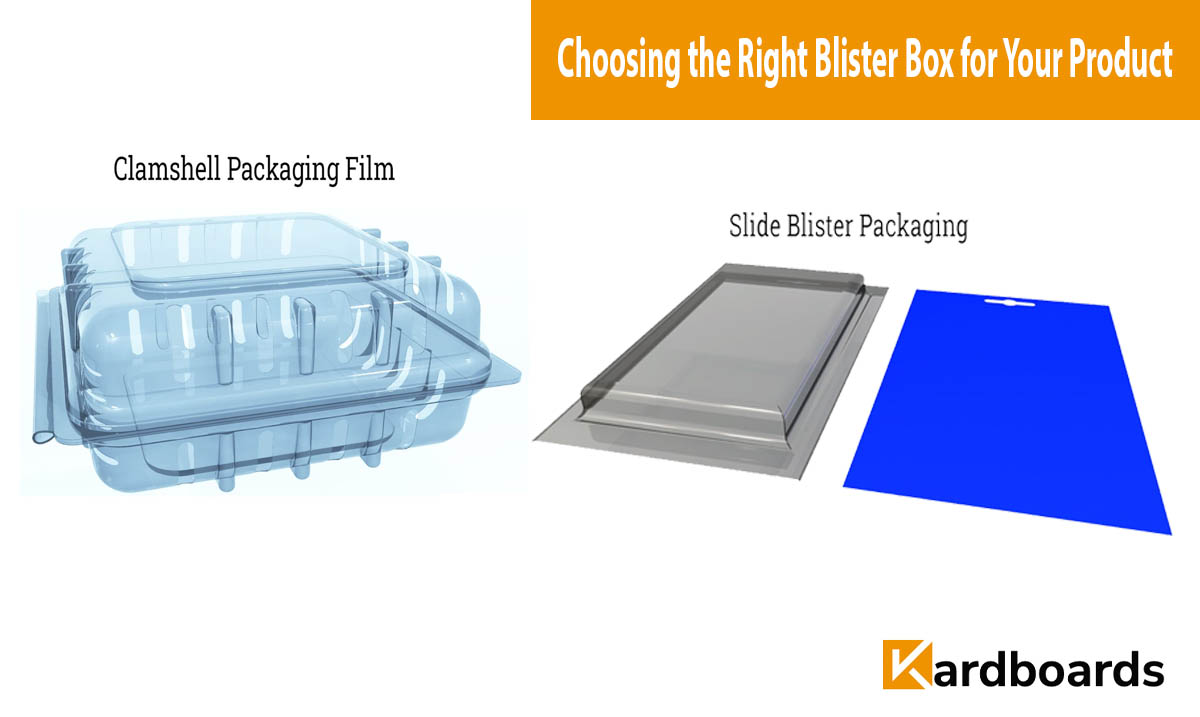
Primary packaging is the material that directly encases and protects the product. It is often what the consumer interacts with first — such as bottles, blister packs, jars, or pouches. This layer also carries key branding and regulatory information.
- Examples: Plastic bottles, aluminum cans, blister trays, sachets, and cartons
- Functions: Product containment, preservation, and user convenience
- Industries: Food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and consumer electronics
Insight: The primary package not only preserves product integrity but also defines shelf appeal — where color, texture, and shape influence buying decisions.
2. Secondary Packaging — Grouping and Brand Presentation
Secondary packaging groups multiple primary packages together for retail display or easier handling. This level serves both protection and marketing purposes — it’s what customers often see on shelves.
- Examples: Folding cartons, display boxes, or multi-pack sleeves
- Functions: Organize, brand, and protect products during transport and sale
- Common materials: Paperboard, corrugated board, or rigid boxes
Kardboards specializes in custom-printed secondary packaging solutions that combine brand storytelling with practical protection, enhancing visibility at retail points.
3. Tertiary Packaging — Bulk Transport and Storage
Tertiary packaging focuses on logistics — the layer that protects products during shipping, warehousing, and distribution. Its purpose is efficiency and durability rather than aesthetics.
- Examples: Corrugated boxes, wooden pallets, shrink wraps
- Functions: Bulk transport, stacking, and load protection
- Materials: Heavy-duty corrugated board, stretch film, pallet straps
Note: Kardboards’ corrugated export boxes are engineered to international shipping standards — combining strength, moisture resistance, and sustainability.
4. Quaternary Packaging — Logistics and Automation Integration
Quaternary packaging is the outermost level, designed for handling large quantities during automated logistics. It includes bulk containers, containers for freight transport, and reusable systems.
- Examples: Freight containers, large crates, reusable plastic totes
- Functions: Facilitate warehouse management, export efficiency, and automation compatibility
- Users: Wholesalers, logistics providers, and manufacturers
By optimizing quaternary packaging, Kardboards helps global supply chains reduce costs and environmental impact while improving traceability.
How the 4 Levels Work Together
The 4 levels of packaging form a connected system — each supporting the other to ensure safe product delivery, consistent branding, and operational efficiency. From primary design to tertiary logistics, Kardboards integrates sustainability and innovation at every step.
Whether it’s retail-ready cartons or export-grade corrugated boxes, every Kardboards solution is crafted to perform across all packaging tiers — meeting the needs of both consumers and global distributors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 4 levels of packaging?
The 4 levels of packaging are Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary. Each plays a unique role in protecting, marketing, and transporting products efficiently.
What is the difference between primary and secondary packaging?
Primary packaging directly encloses the product, such as bottles or blister packs. Secondary packaging groups multiple primary packages for display or handling, like cartons or sleeves.
Why is tertiary packaging important?
Tertiary packaging protects bulk products during shipping and storage. It ensures safe stacking, minimizes damage, and optimizes logistics.
What does quaternary packaging include?
Quaternary packaging includes large-scale containers and systems used for handling, storage, and export — such as freight crates and reusable bins.
How does Kardboards support all packaging levels?
Kardboards designs packaging solutions across all four levels — from consumer-facing boxes to industrial export containers — ensuring quality, sustainability, and brand consistency.